
Nevertheless, with a longer sample time-say, ten minutes of data rather than 30 seconds-PPG data is sometimes clear enough to distinguish the rhythm visually. For Apple Watch on WatchOS 2.2, the highest resolution currently available is an average heart rate every five seconds.
#Cardiograph bpm series
What’s more, most wearables analyze the raw PPG time series and then report an averaged heart rate (e.g., 76 beats per minute) to app developers. You can’t see P waves or the intervals (PR, QS, QT) which give detailed clues about electrical conduction within different types of cardiac tissue.

The drawback of PPG is that it only measures a pulse wave.
#Cardiograph bpm skin
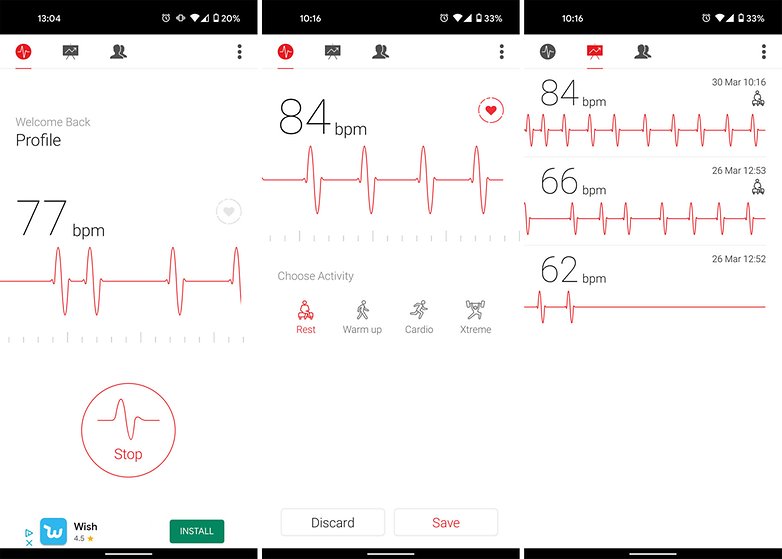
Apple Watch measures those pulse waves at the wrist, but anywhere on the skin with good blood perfusion-e.g., your forehead, arm, chest, ear lobes-can be used to measure heart rate. Every time your heart beats, it sends a pulse wave throughout your arteries. Ĭonsumer heart rate sensors, such as the Apple Watch, use an optical sensor based on photoplethysmography (PPG). For example, if the QRS complex precedes or obscures the P wave, it indicates electrical impulses in the heart are traveling in reverse (from ventricles to AV node to atria), which can happen in a common arrhythmia called supraventricular tachycardia. ĮCG (one heart beat) vs PPG (four heart beats)Ī cardiologist can infer quite a lot from even a short ECG reading. In normal heart rhythm, every QRS complex follows a P wave. Specialized electrical tissue called the AV node causes a 120–200ms delay, and then the bottom two chambers of the heart (the ventricles) contract, producing a larger voltage spike called the QRS complex. In every normal heart beat, the top two chambers of the heart (the atria) contract first, producing a small voltage notch called the P wave. The gold standard in a hospital setting is an electrocardiogram, or ECG, which shows the voltage within your heart’s electrical system. Key Background: ECG vs PPGīefore explaining the details of the abnormal rhythms, it helps to have a little background on the two most common types of heart rate sensors. And atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter show that abnormal heart rhythms can range from chaotic to almost mechanically regular. While stressed during rush hour traffic, your heart rate can rise past 120 bpm- about as high as playing hockey-with a fast, wave-like variation. For example, in restful sleep, there’s a heart rate spike every 90 minutes or so (those are your REM cycles) between those spikes, there are smaller periodic fluctuations. Each vertical bar shows average heart rate over 5 seconds.Įven in normal rhythm, heart rate is highly variable. Heart rates recorded on Apple Watch using Cardiogram. The frequency and depth of variation reflects nearly everything that happens in your life, including your level of physical activity, emotional state, and whether you’re sleeping or waking.įor example, here are six examples of normal heart rhythm (columns 1–3) and two abnormal rhythms (column 4) from Cardiogram for Apple Watch: In fact, it’s regularly irregular: your heart rate varies periodically due to your breathing rate and autonomic nervous system. That’s not quite right, because a normal pulse is irregular. Sometimes people say “irregular pulse” as a shorthand for an abnormal heart rhythm.
Please don’t take any of the below as medical advice.

Note: although we believe wearables can save lives-and hope to play a part in making that happen-there is a lot of clinical groundwork that needs to happen first. As part of the mRhythm Study, we’re analyzing a lot of heart rate data, and decided to write a brief primer on what both normal and abnormal heart rhythms look like when measured on an Apple Watch.ĭownload Cardiogram for your Apple Watch, Fitbit, wearOS, or Garmin watch here: What do normal and abnormal heart rhythms look like on Apple Watch?Īlmost every month, a news story pops up about somebody whose life was saved by their Apple Watch.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
